What is GPON technology?
GPON (Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network) represents the pinnacle of technology deployed by telecommunication operators to bring optical fiber into our daily lives.
This technology, which now extends to the core of building network infrastructures, is acclaimed for its numerous benefits, both operationally and competitively. Among its major advantages, optical fiber stands out for its ability to significantly enhance connectivity while actively contributing to reducing the ecological footprint.
GPON, the eco-friendly performance fiber
Optimal performance ensuring prolonged durability
- Speeds of up to 10 Gbit/s
- Significantly improved security
- Operational cost reduction of up to 75%
Optimizations for a better carbon footprint
- Reduction in energy consumption by up to 60%
- Elimination of cooling systems, UPS, and repeaters
- Up to 75% space savings in technical rooms
- Fiber and splitters longevity of up to 40 years.
This technology represents a long-term investment, using fewer electrical components and significantly reducing overall energy consumption.
Discover the GPON technology that reduces your power consumption by up to 60%!
GPON technology is widely acclaimed for its many benefits, both in operational and competitive terms. Among its major assets, fiber optics stands out for its ability to significantly improve connectivity, while actively contributing to the reduction of your ecological footprint and energy efficiency.
The ecological contributions of GPON (Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network)
GPON, also known as POL (Passive Optical LAN) for its specific deployment within buildings, marks an ecological turning point in computer networks by replacing switches and routers with passive optical splitters.
These components, devoid of electronic elements, require neither cooling systems nor UPS, and their lifespan is measured in decades.
Optical fiber allows for cabling distances of up to 20km, significantly reducing the need for repeaters. This technology is therefore not only a major advancement for operational savings but also for reducing carbon footprint.
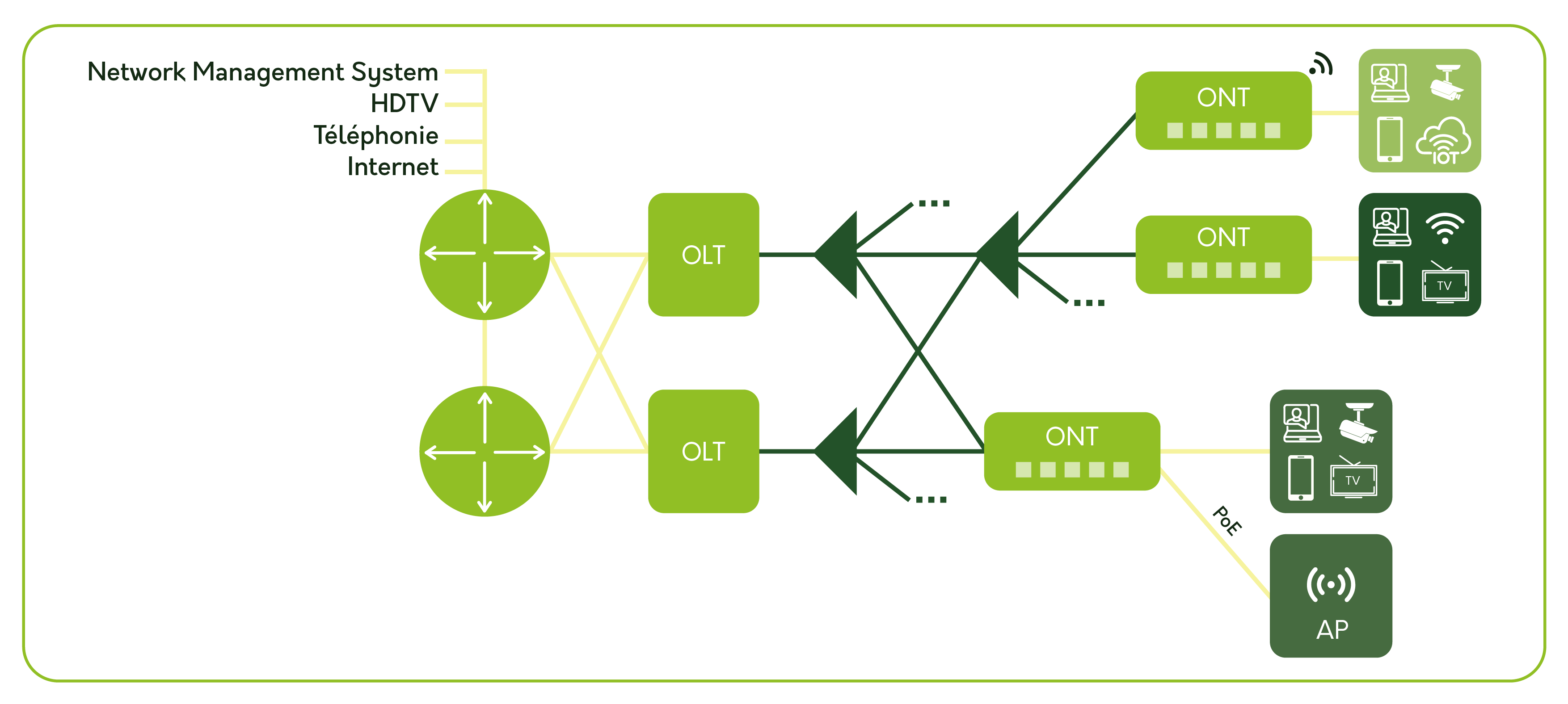
The components of a GPON architecture.
The core of the GPON architecture consists of the OLT (Optical Line Termination), which distributes the streams to the ONTs (Optical Network Terminations), connected to the terminals. Between the OLT and the ONT, optical splitters multiply the streams, offering a flexible and scalable network architecture.
Fiber takes up 80% less space than copper lines, allowing for a discreet integration of the infrastructure, for example, in false ceilings. Complete network redundancy then becomes completely transparent to residents.
Technological sustainability and enhanced security through GPON
GPON benefits from mature technology, evolving with telecom industry standards. This maturity ensures compatibility across different versions and optimizes investments.
In terms of security, GPON uses separate wavelengths for upstream and downstream traffic, with AES128 encryption to protect data.
Ecodesign and lifecycle improvement
Regardless of the technology, whether copper or fiber, Green WiFi’s principles of eco-responsibility apply to the design of the architecture, deployment, and operation of these networks and associated terminals:
Optimization for availability and performance
Rationalization of electronic devices
Economy and sustainability of devices
The other Green WiFi solutions
With Green WiFi, you choose responsible technological solutions for a high-performing and planet-friendly digital world.
